[ad_1]
Server-side Ad Insertion (SSAI)
Server-Side Ad Insertion (SSAI) is a technology for seamlessly stitching commercials into a video stream on a server side before it is loaded on a viewer’s device. As a result, users get a single stream from a server, and no matter how they watch the content, either with their browsers, apps, or any other way, SSAI produces uninterrupted video with ads with almost zero delays.
How server-side video ad insertion works?
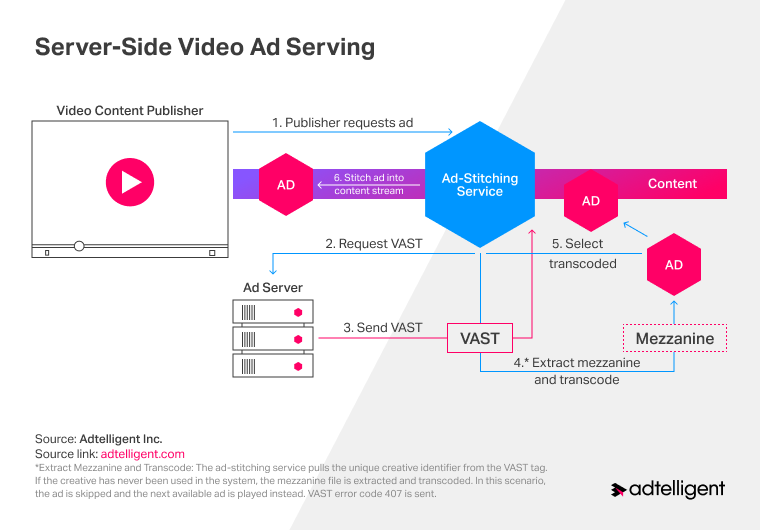
The whole process consists of six steps:
- Video content publisher requests for VAST at Ad Stitching Service.
- The Ad Stitching Service initiates the request for the ad server to get the VAST tag.
- The ad server transmits the VAST tag and an ad file for showing and mezzanine. Suppose an ad has already been obtained during the sequence before that, and the file for showing is of the correct format and can be inserted in a video stream. In that case, the system goes to step 5. However, if the obtained VAST tag is a Wrapper one, the Ad Stitching Service extracts an internal response.
- Ad Stitching Service gets the ad ID from the received VAST tag. If this ad was not used before, the system transcodes the mezzanine, the commercial is ignored, and the following ad for displaying is loaded.
- Selecting a transcoded file: In case a commercial in VAST tag corresponds to the ad ID for the commercial, which was transcoded, the system chooses a processed file, which is loaded in memory.
- Ad Stitching Service sews the processed ad to the video stream and transmits this mix to the video player on the client’s side.
The following diagram shows how an ad is inserted in the streaming video using SSAI technology.
The SSAI operation principle is as follows:
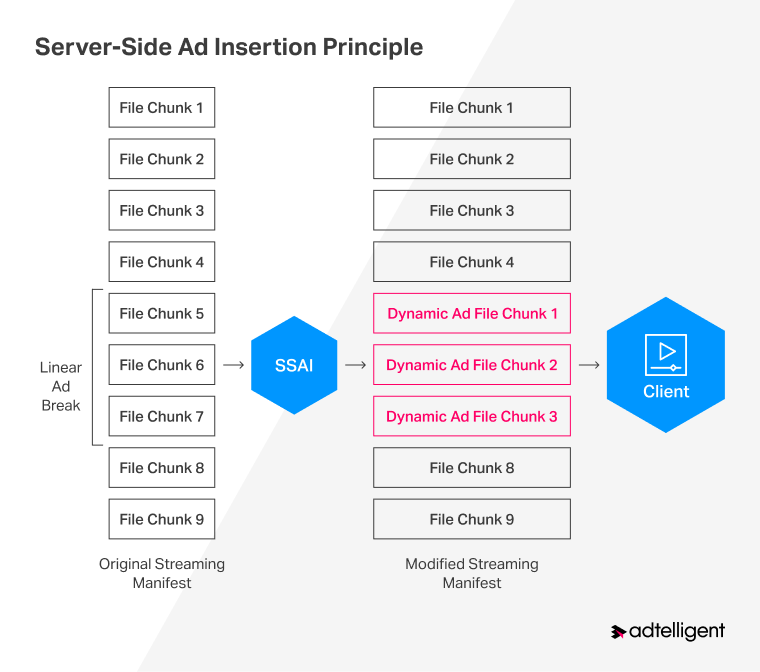
Server-side ad insertion enables complete correspondence between the bitrate of advertising and video content in contrast to client-side ad insertion, where ads tend to be lower quality than primary content, resulting in a poor watching experience. According to the survey, over 60% of respondents admit they’re highly annoyed when brands blast generic ad messages that don’t pertain to them. By offering personalized ads, agencies, and marketing teams can address segmented markets better and ensure revenue growth with relevant advertising instead of being untargeted to a disinterested audience.
How SSAI vendors deliver seamless and buffer-free video ads
SSAI vendor is an intermediate between the online video player and the advertising server. They provide technological means for the implementation of SSAI, and they perform the following functions:
- identification of ad breaks in video flow;
- limiting buffering by using adaptive bitrate;
- transcoding ads to exclude buffering from video streams with proper adaptive bit rate formats;
- inserting ads and stitching the ad and video content together;
- communicating with the player.
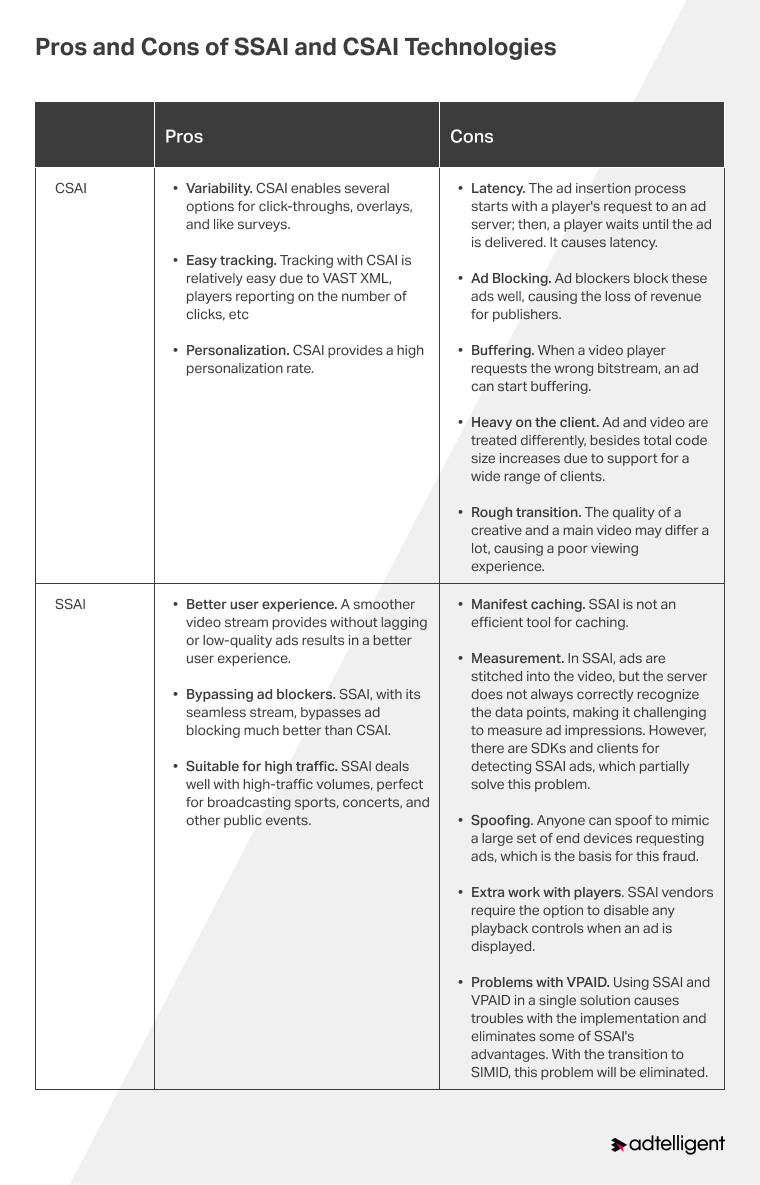
Benefits and drawbacks of SSAI and CSAI
SSAI is often compared to another popular ad insertion technology, CSAI (client-side ad insertion). The conceptual difference between SSAI and CSAI is on the side where the video stream is processed and advertising is inserted: on a server-side (in SSAI) and on a client-side (CSAI). In the case of CSAI, ads are separated from the main video. In terms of delivery, they are played independently of each other. Meanwhile, server-side ad solutions are less complex in development and management and less likely to crash.
Here are the main benefits and drawbacks of each of these technologies:
Bypassing ad blockers
To avoid ads, people actively use ad blockers. In most cases, these applications effectively block different ads, which has become a massive problem for publishers. According to a recent report by Backlinko data, about 40% of Internet users use specific software to block ads. Unlike traditional client-side methods like VAST and VPAID, which combine advertising and non-advertising content on the client side, server-side ad insertion inserts ads at the content-management system level. The benefit of using SSAI is that the client receives a seamless stream from a single source, creating a broadcast-like transition between ads and content.
As a rule, ad blockers check and block any requests to ad servers and all content (advertising) that comes from them. But in the case of SSAI, the received video already contains ad inserts, and no requests are made to any ad server from the client side, so the program does not block the ad that goes with the main video.
Privacy issue
The laws aimed at personal data protection: GDPR (in Europe) and CCPA (in the USA), have caused a challenge for publishers: how to provide users with original, relevant advertising while complying with the requirements to ensure data privacy. In the case of client-side ad insertion, the client’s IP addresses and cookies are disclosed, which means third parties can track such users.
The implementation of SSAI solves this problem. The system is an intermediary between a user and an advertiser, allowing publishers to control data transmission from a viewer to an advertising ecosystem while maintaining the customer’s viewing experience. Thus, on the one hand, SSAI provides the personalization of advertising and, on the other hand, anonymizes personal data per private data protection regulations.
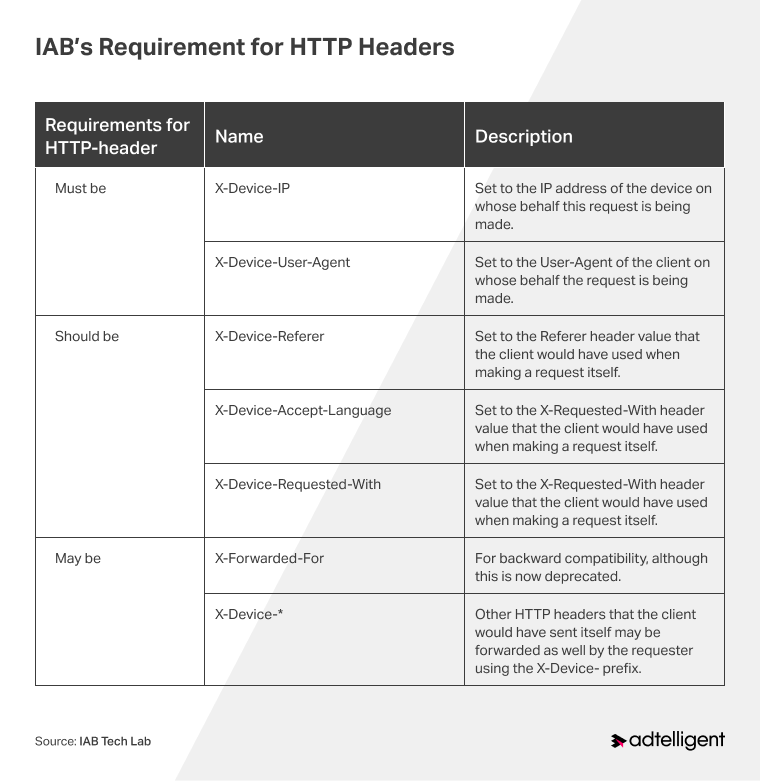
SSAI requirements
In its VAST 4.3 specification, the IAB provides precise requirements for which HTTP headers should include, which should be included, and which can be included when using SSAI.
SSAI for LiveTV and VOD
Video-on-demand (VOD) streams and LiveTV broadcasters who use a CSAI solution need help maintaining, especially considering the rising number of viewers. Many of them consider transferring to the SSAI approach. This is due to the proven efficiency of server-side ad insertion for LiveTV. Here are the main reasons for that:
- Flexibility. In SSAI, the executed code is not tied to an ad server; video and ad stitching go on a server-side, and inventory and decision-making are separated from the content delivery to users, providing overall flexibility to the process.
- Controlling. A single spot for all ad insertion requests in LiveTV and VOD, and a single interface to access the set of streams and VOD provide better control over the process.
- Interactivity. SDKs are available for SSAI supporting clickable linear content and overlays; publishers can set the instances during pauses, skipping, and seeking.
Thus SSAI provides considerable benefits for LiveTV and VoD providers, which results in its rising popularity among the representatives of this niche.
Transparency and fraud issues with SSAI on OTT/CTV
No matter how efficient it is from an ad-serving point of view, the SSAI vendor stitching together video streams creates an additional layer between a publisher’s tech stack and the end user’s device, which makes SSAI inherently more vulnerable to fraud.
The most reliable fix is authorizing all supply and bid requests with trusted tech partners that can offer transparency. The IAB Tech Lab introduced its sellers.json spec in 2019 to help buyers vet the supply source and announced a version of the Open Measurement SDK specifically to validate CTV impressions.
Generally, adopting IAB Tech Lab’s VAST standards and macros is the quickest way to increase transparency and efficiency when using SSAI.
SSAI is the future of ad monetization
The improved user experience provided by SSAI technology due to its seamless video stream can significantly increase revenue for media owners providing their content. According to estimates by Mordor Intelligence, the online advertising industry will reach $980 billion by 2025. With server-side ad insertion, publishers, like OTT platforms, CTV providers, TV Broadcasters, and VOD broadcasters, get a significant advantage over those competitors using CSAI. Thanks to SSAI advantages, including the ability to bypass ad blockers and the high quality of the finished video, it’s a promising technology. But It will take some time for buyers to become more comfortable using SSAI-based solutions using new metrics and expand significantly. This shift in the industry will pave the way for exciting innovations such as interactive ads and in-content or in-app purchases.
Frequently asked questions
In what case is CSAI better than SSAI?
In most cases, CSAI is easier to set up, solutions based on this technology are cheaper, and their performance is estimated easier. So when you need a quick, affordable, and easily tracked solution, CSAI is better.
When can we use Server Side Ad Insertion?
In case when the maximum quality of the video stream is required and if most consumers use ad blockers on their devices.
What devices can support SSAI?
Any modern device for playing video over the Internet is compatible with SSAI technology. These are desktop PCs, mobile devices, and Сonnected TVs.
Is SSAI beneficial for live inventory and events?
SSAI is an excellent solution for any media owner transitioning from the traditional linear space. Server-side ad insertion can be used to replace traditional ad breaks with digital ads, whether the event is live or pre-recorded.
Can you match cookied users in SSAI environments since an additional partner is involved?
In most cases, no, but some solutions allow synchronizing users in the SSAI web environment.
What’s wrong with client-side ad insertion?
It provides a worse user experience due to latency and bit rate differences between video ads and content. Ad blockers block its ads much more often than SSAI.
What is DAI?
Dynamic Ad Insertion (DAI) is a technology that allows ads to be dynamically inserted into a video stream. This is the first server-side ad insertion solution that will enable you to dynamically add ads to live broadcasts, linear programs, and video-on-demand.
What is OTT header bidding?
Similar to other header bidding techniques, OTT header bidding allows publishers to provide the inventory to several demand sources simultaneously before the request is sent to their ad server.
[ad_2]
Source link